ACNE
Need An Appointment?
Drop Your Number here
Acne: Causes, Types, and Effective Treatment Options
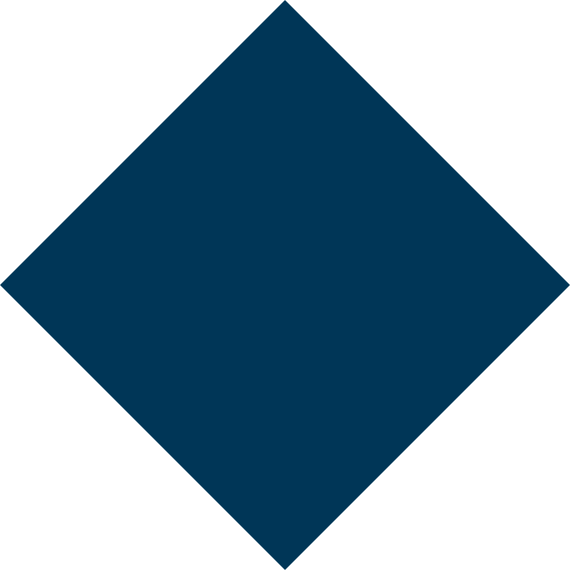
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions worldwide, affecting teenagers and adults alike. It occurs when the skin’s pores become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, or bacteria, leading to pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, or cysts. While acne is not a serious health threat, it can cause discomfort, scarring, and emotional distress. The good news is that with the right treatment and skincare routine, acne can be managed and prevented effectively.
Types of Acne
Acne can appear in different forms depending on its severity and depth within the skin:
-
Whiteheads (Closed Comedones):
Small, white bumps formed when pores are completely clogged with oil and dead skin. -
Blackheads (Open Comedones):
Open pores filled with excess oil that darken when exposed to air. -
Papules:
Small, red, inflamed bumps without visible pus. -
Pustules (Pimples):
Red bumps filled with pus at the tip, often painful to touch. -
Nodules:
Large, hard, and painful lumps deep under the skin, indicating severe inflammation. -
Cystic Acne:
The most severe form, characterized by pus-filled cysts that can cause scarring.
Causes of Acne
Several factors contribute to acne formation, including:
-
Hormonal Changes: Increased androgen levels during puberty, menstruation, or pregnancy stimulate excess oil production.
-
Excess Sebum Production: Overactive oil glands clog pores easily.
-
Bacteria (Cutibacterium acnes): Bacteria inside blocked pores cause infection and inflammation.
-
Clogged Pores: Dead skin cells that aren’t shed properly block hair follicles.
-
Diet: High consumption of dairy products, sugar, or greasy foods may worsen acne.
-
Stress: Triggers hormonal changes that can aggravate breakouts.
-
Medications: Certain steroids, birth control pills, or lithium can cause acne-like eruptions.
-
Cosmetic Products: Heavy or oily skincare products can block pores and lead to “cosmetic acne.”
1.jpg)
Treatment Options for Acne
Acne treatment depends on the severity of the condition and skin type. A combination of medical treatments and proper skincare often gives the best results.
1. Topical Treatments
-
Benzoyl Peroxide: Kills bacteria and reduces inflammation.
-
Retinoids (Adapalene, Tretinoin): Help unclog pores and promote cell renewal.
-
Salicylic Acid: Gently exfoliates and prevents pore blockage.
-
Topical Antibiotics: Reduce bacteria and inflammation.
These medications are commonly prescribed for mild to moderate acne.
2. Oral Medications
-
Antibiotics: Used to control bacterial growth in moderate to severe acne.
-
Hormonal Therapy: Birth control pills or anti-androgen medications (like spironolactone) help regulate hormonal acne in women.
-
Isotretinoin (Accutane): A powerful medication for severe, cystic acne that doesn’t respond to other treatments.
All oral medications should be used under a dermatologist’s supervision.
3. Advanced Treatments
-
Chemical Peels: Help remove dead skin and reduce scars.
-
Laser and Light Therapy: Target bacteria and reduce oil production.
-
Microneedling: Stimulates collagen production to minimize acne scars.
-
Photodynamic Therapy: Reduces severe acne by shrinking oil glands.
4. Skincare Routine
A consistent skincare routine is key to controlling acne:
-
Use a gentle cleanser twice daily.
-
Apply oil-free moisturizers to prevent dryness.
-
Use non-comedogenic (non-pore-clogging) products.
-
Always remove makeup before bed.
-
Apply sunscreen daily to prevent dark spots and scars.
Need An Appointment?
Drop Your Number here
Symptoms of Acne
-
Pimples, whiteheads, or blackheads on the face, neck, chest, or back
-
Redness and inflammation around affected areas
-
Painful nodules or cysts under the skin
-
Dark spots or scars after healing
-
Oily skin or visible enlarged pores
The severity of acne can range from mild to severe, and early intervention helps prevent long-term scarring.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Tips
While medical treatments are essential, home remedies and lifestyle changes can complement acne care:
-
Drink plenty of water to flush out toxins.
-
Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids.
-
Avoid touching or popping pimples to prevent scarring.
-
Manage stress through yoga or meditation.
-
Change pillowcases and towels frequently to avoid bacterial buildup.
Prevention and Aftercare
Preventing acne involves maintaining a clean, healthy skincare routine and avoiding triggers. Regular dermatology visits help monitor progress and adjust treatments as needed. After acne heals, treatments like chemical peels, microneedling, or laser resurfacing can help fade scars and even out skin tone.
Conclusion
Acne is a common yet highly treatable skin condition. By understanding its causes and choosing the right treatments, you can achieve clear, smooth, and healthy skin. Whether it’s mild breakouts or severe cystic acne, a dermatologist can help design a personalized treatment plan. Remember — patience and consistency are key to long-lasting acne control and confident, glowing skin.
Patient's Testimonials

Reviews & Treatment Results at Bansal Skin Solution

5.0
(600 Reviews)

5.0
(500 Votes)

5.0
(567 Votes)
She's the best skin doctor I've come across so far. she listens patiently, gives the prominent treatment accordingly. Guys looking for skin treatment must visit Dr Nidhi Bansal, you will get satisfying results👍

Ravi Bhardwaj
PatientI consulted with Dr Nidhi Bansal after one of my friend suggested. The doctor is very calm and well versed with the solutions. I definitely liked the way He made me understand the issues of my hair sclap. I am very happy with my own experience with her and the treatment provided amazing hence I would highly recommend to this doctor for any skin or hair disease.

Manish Pal
PatientI was suffering from severe acne on my face. Dr Nidhi told me in detail about the treatment options and customized the procedures for my face. Within one day my redness and acne has reduced by 90%. I am so happy with the results and would recommend Dr Nidhi to everyone for their skin and hair problems.

Kartikey Singh
PatientBest doctor I always go to Dr Nidhi skin clinic whenever i have any skin problems . Dr. Nidhi is such a humble + trusted doctor I was dealing with pimples and scars from 6 years, someone told me about Dr Nidhi .I having been taking treatment from 2 months .my acne has gone for forever ,thanks for giving me normal skin best dermatologist in jaipur I got 100 % results , M bhut jayda preshan tha acne , blackheads whiteheads se ,mera face bhut khrab dikhta tha bhut guilty feel hota tha logo ko face krne m now I m confident .thank you doctor