Milia

Need An Appointment?
Drop Your Number here
Milia: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
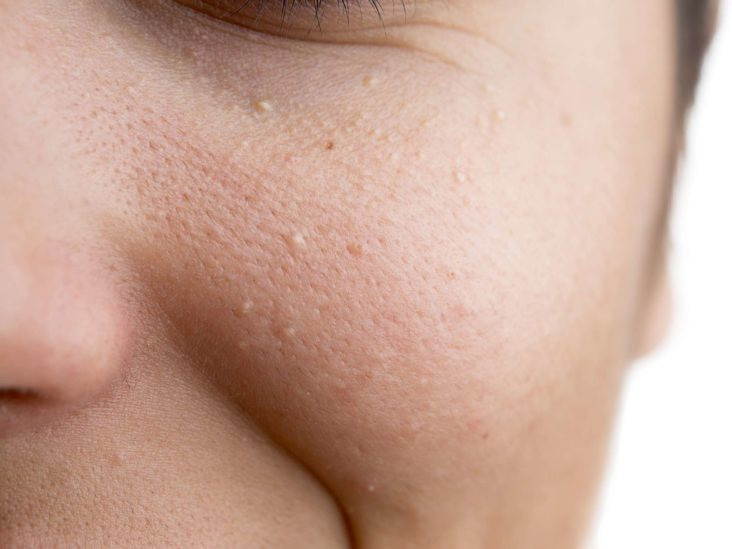
Milia are small, white or yellowish bumps that commonly appear on the face, particularly around the eyes, cheeks, or nose. Although harmless, these tiny cysts can be frustrating for many people who want clear, smooth skin. Milia often occur when dead skin cells or keratin get trapped beneath the skin’s surface. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you manage and prevent them effectively.
Causes of Milia
Milia can develop in people of all ages — from newborns to adults. The causes vary depending on age and skin type.
1. In Newborns (Neonatal Milia)
Milia are extremely common in newborn babies and affect about 50% of infants. They usually appear on the nose, cheeks, or forehead and disappear naturally within a few weeks. The cause is unknown but is believed to be due to immature sweat glands.
2. In Children and Adults (Primary Milia)
In older children and adults, milia occur when dead skin cells become trapped in small pockets on the skin’s surface instead of shedding naturally. Common triggers include:
-
Sun damage
-
Heavy or oil-based skincare products
-
Poor exfoliation habits
-
Skin injuries or burns
-
Use of steroid creams
-
Long-term use of thick makeup or sunscreen
3. Secondary Milia
These occur after skin damage, such as burns, rashes, blistering, or laser treatments. When the skin heals, keratin can become trapped under the new surface layer, leading to milia formation.
1.jpg)
Types of Milia
There are several types of milia, classified based on their cause and appearance:
-
Neonatal Milia: Common in newborns; disappear without treatment.
-
Primary Milia: Develop spontaneously in children and adults.
-
Secondary Milia: Result from skin injury or irritation.
-
Multiple Eruptive Milia: Appear suddenly in clusters, often on the face, upper arms, or torso.
-
Traumatic Milia: Occur after skin trauma like burns, rashes, or excessive exfoliation.
Treatment Options for Milia
Milia often resolve on their own, but persistent or widespread cases may need professional treatment. Here are the most effective options:
1. Professional Extraction
Dermatologists use a sterile needle or a fine blade to gently open the surface of the skin and extract the milia. This should never be done at home to avoid scarring or infection.
2. Chemical Peels
Mild chemical peels using glycolic acid or salicylic acid help remove dead skin cells, unclog pores, and promote healthy cell turnover, preventing future milia formation.
3. Laser Treatment
In stubborn or recurring cases, dermatologists may use laser therapy (like CO₂ laser) to remove deeper milia safely without damaging surrounding skin.
4. Retinoid Creams
Topical retinoids (vitamin A derivatives) such as tretinoin help exfoliate the skin, promoting cell turnover and reducing the risk of milia recurrence.
5. Cryotherapy
This treatment involves freezing the milia with liquid nitrogen, causing them to dry up and fall off naturally. It’s safe and effective when done by a professional.
Need An Appointment?
Drop Your Number here
Symptoms of Milia
Milia are easy to recognize by their distinct appearance:
-
Small (1–2 mm) dome-shaped white or yellowish bumps
-
Firm to the touch and not painful
-
Do not contain pus or redness (unlike acne)
-
Commonly appear around the eyes, nose, cheeks, and forehead
They are purely cosmetic and do not indicate infection or serious skin problems.
Home Remedies and Skincare Tips
If your milia are mild, proper skincare can help prevent or minimize their appearance:
-
Exfoliate regularly: Use gentle exfoliants like lactic acid or salicylic acid to remove dead skin cells.
-
Use non-comedogenic products: Avoid heavy creams or oil-based cosmetics that can clog pores.
-
Cleanse twice daily: Keep your face clean to prevent buildup.
-
Avoid picking or squeezing: This can cause infection or permanent scars.
-
Moisturize properly: Use lightweight, water-based moisturizers to maintain hydration without blocking pores.
-
Protect your skin from the sun: Sun damage can thicken skin and worsen milia formation. Always wear SPF 30 or higher.
Prevention Tips
To reduce the chances of developing milia:
-
Avoid using greasy or thick skincare products.
-
Incorporate mild exfoliation into your weekly routine.
-
Remove makeup before sleeping.
-
Avoid excessive use of topical steroid creams.
-
Keep skin hydrated and protected with sunscreen.
When to See a Dermatologist
If your milia do not go away within a few weeks, spread across large areas, or cause cosmetic concern, consult a dermatologist. Professional extraction or specialized treatments can help remove them safely and prevent recurrence.
Conclusion
Milia are harmless yet bothersome small bumps that can affect anyone. They may resolve naturally, but in persistent cases, professional dermatological care offers quick and effective removal. Maintaining a good skincare routine, exfoliating regularly, and protecting your skin from the sun are the best ways to keep your complexion clear, smooth, and healthy.
Patient's Testimonials

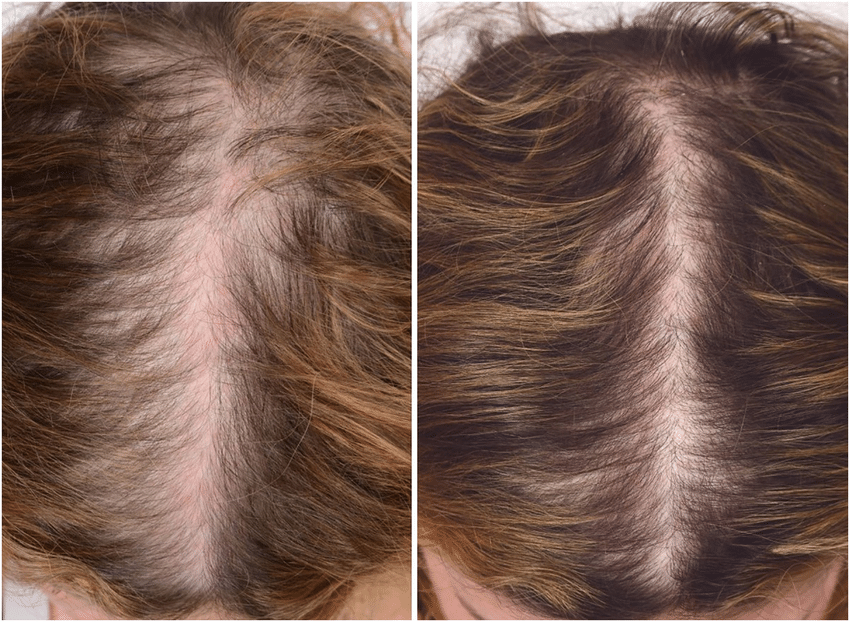
Reviews & Treatment Results at Bansal Skin Solution

5.0
(600 Reviews)

5.0
(500 Votes)

5.0
(567 Votes)
She's the best skin doctor I've come across so far. she listens patiently, gives the prominent treatment accordingly. Guys looking for skin treatment must visit Dr Nidhi Bansal, you will get satisfying results👍

Ravi Bhardwaj
PatientI consulted with Dr Nidhi Bansal after one of my friend suggested. The doctor is very calm and well versed with the solutions. I definitely liked the way He made me understand the issues of my hair sclap. I am very happy with my own experience with her and the treatment provided amazing hence I would highly recommend to this doctor for any skin or hair disease.

Manish Pal
PatientI was suffering from severe acne on my face. Dr Nidhi told me in detail about the treatment options and customized the procedures for my face. Within one day my redness and acne has reduced by 90%. I am so happy with the results and would recommend Dr Nidhi to everyone for their skin and hair problems.

Kartikey Singh
PatientBest doctor I always go to Dr Nidhi skin clinic whenever i have any skin problems . Dr. Nidhi is such a humble + trusted doctor I was dealing with pimples and scars from 6 years, someone told me about Dr Nidhi .I having been taking treatment from 2 months .my acne has gone for forever ,thanks for giving me normal skin best dermatologist in jaipur I got 100 % results , M bhut jayda preshan tha acne , blackheads whiteheads se ,mera face bhut khrab dikhta tha bhut guilty feel hota tha logo ko face krne m now I m confident .thank you doctor