Psoriasis

Need An Appointment?
Drop Your Number here
Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
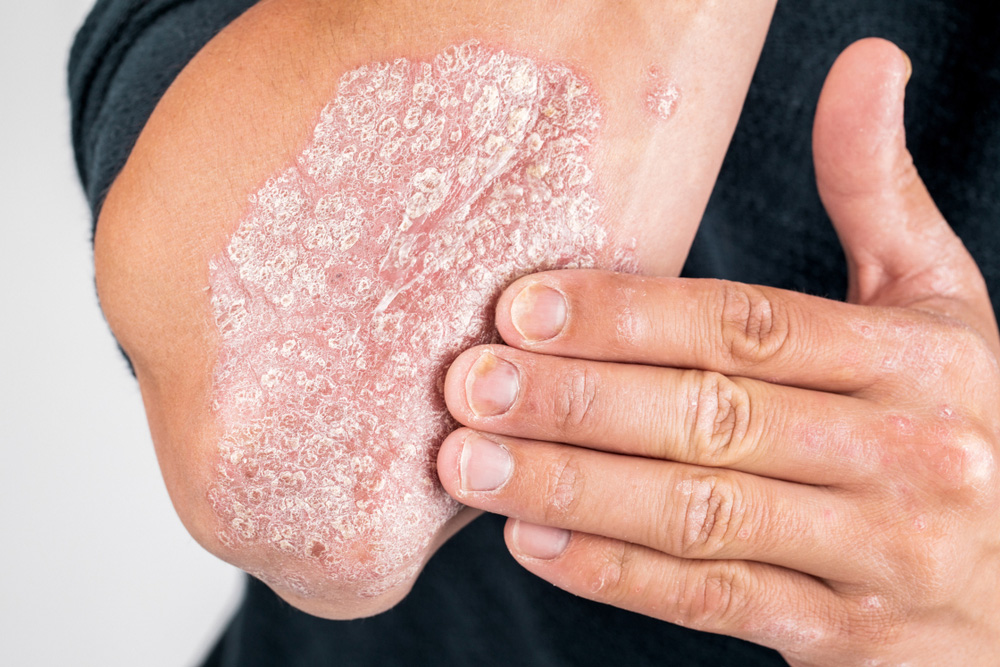
Psoriasis is a long-term (chronic) skin disorder that causes the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to thick, red, scaly patches on the surface of the skin. It is a non-contagious autoimmune condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. The condition tends to flare up in cycles — symptoms may worsen for a few weeks or months, then subside for a while before returning.
While there is no permanent cure for psoriasis, effective treatments can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve the appearance and health of the skin.
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but several factors can trigger or worsen the condition:
-
Immune System Dysfunction:
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder in which immune cells mistakenly attack healthy skin cells, causing rapid growth and inflammation. -
Genetic Predisposition:
A family history of psoriasis increases the risk of developing the condition. -
Environmental Triggers:
Factors such as cold weather, pollution, and dry air can worsen symptoms. -
Stress:
High stress levels can trigger flare-ups or make existing symptoms worse. -
Infections:
Throat infections (like strep throat) or skin infections can trigger psoriasis, especially in children. -
Medications:
Certain drugs such as beta-blockers, lithium, and antimalarials may induce or worsen psoriasis. -
Lifestyle Factors:
Smoking, alcohol consumption, and obesity are known to aggravate psoriasis.
.jpg)
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, each with distinct symptoms and areas of occurrence:
-
Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris):
The most common form, characterized by raised, red patches with silvery-white scales. Commonly found on the scalp, elbows, knees, and back. -
Guttate Psoriasis:
Small, drop-shaped sores that usually appear after throat infections. Common in children and young adults. -
Inverse Psoriasis:
Occurs in skin folds such as under the breasts, armpits, or groin. The skin appears smooth, shiny, and red. -
Pustular Psoriasis:
Characterized by white pustules (blisters filled with pus) surrounded by inflamed skin. -
Erythrodermic Psoriasis:
The most severe and rare form, causing widespread redness, itching, and scaling that can be life-threatening if untreated. -
Nail Psoriasis:
Affects fingernails and toenails, leading to discoloration, thickening, and pitting. -
Scalp Psoriasis:
Causes red, scaly patches on the scalp, often mistaken for dandruff.
Need An Appointment?
Drop Your Number here
Symptoms of Psoriasis
The symptoms of psoriasis vary depending on the type and severity but generally include:
-
Thickened, scaly patches of skin
-
Redness and inflammation
-
Itching, burning, or soreness
-
Cracked, dry skin that may bleed
-
Discolored or pitted nails
-
Joint pain and stiffness (in psoriatic arthritis)
Psoriasis most commonly affects the scalp, elbows, knees, back, and nails, though it can occur anywhere on the body.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
A dermatologist can usually diagnose psoriasis through a physical examination of the skin, scalp, and nails. In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other skin conditions such as eczema or fungal infections.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
Although psoriasis has no cure, effective treatments can help control symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Treatment depends on the severity and type of psoriasis:
1. Topical Treatments
These are creams and ointments applied directly to the skin to reduce inflammation and scaling.
-
Corticosteroid creams
-
Vitamin D analogs (Calcipotriol)
-
Coal tar and salicylic acid
-
Moisturizers and emollients to prevent dryness
2. Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light helps slow down skin cell growth and reduce inflammation.
3. Oral and Injectable Medications
For moderate to severe cases, systemic treatments may be prescribed:
-
Methotrexate and Cyclosporine to suppress immune response
-
Biologic drugs such as Adalimumab, Etanercept, and Secukinumab that target specific immune system pathways
4. Lifestyle & Home Remedies
-
Regular moisturizing to prevent dryness
-
Gentle skincare routine with mild soaps
-
Avoid scratching or picking scales
-
Stress management through yoga or meditation
-
Healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids
Complications
If untreated, psoriasis can lead to complications such as:
-
Psoriatic Arthritis: Joint pain and stiffness
-
Depression and Anxiety: Due to cosmetic concerns
-
Skin Infections: From scratching or cracked skin
-
Increased Risk of Diabetes or Heart Disease due to chronic inflammation
Patient's Testimonials

Reviews & Treatment Results at Bansal Skin Solution

5.0
(600 Reviews)

5.0
(500 Votes)

5.0
(567 Votes)
She's the best skin doctor I've come across so far. she listens patiently, gives the prominent treatment accordingly. Guys looking for skin treatment must visit Dr Nidhi Bansal, you will get satisfying results👍

Ravi Bhardwaj
PatientI consulted with Dr Nidhi Bansal after one of my friend suggested. The doctor is very calm and well versed with the solutions. I definitely liked the way He made me understand the issues of my hair sclap. I am very happy with my own experience with her and the treatment provided amazing hence I would highly recommend to this doctor for any skin or hair disease.

Manish Pal
PatientI was suffering from severe acne on my face. Dr Nidhi told me in detail about the treatment options and customized the procedures for my face. Within one day my redness and acne has reduced by 90%. I am so happy with the results and would recommend Dr Nidhi to everyone for their skin and hair problems.

Kartikey Singh
PatientBest doctor I always go to Dr Nidhi skin clinic whenever i have any skin problems . Dr. Nidhi is such a humble + trusted doctor I was dealing with pimples and scars from 6 years, someone told me about Dr Nidhi .I having been taking treatment from 2 months .my acne has gone for forever ,thanks for giving me normal skin best dermatologist in jaipur I got 100 % results , M bhut jayda preshan tha acne , blackheads whiteheads se ,mera face bhut khrab dikhta tha bhut guilty feel hota tha logo ko face krne m now I m confident .thank you doctor