Eczema

Need An Appointment?
Drop Your Number here
Eczema: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It causes the skin to become dry, itchy, red, and inflamed. Though it is not contagious, eczema can significantly affect a person’s comfort and confidence. Understanding its causes, triggers, and treatments can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups effectively.
Causes of Eczema
There’s no single cause of eczema. However, several factors contribute to its development:
-
Genetic Factors:
People with a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop the condition. This genetic link affects the skin’s ability to retain moisture, leading to dryness and irritation. -
Immune System Overreaction:
In eczema patients, the immune system reacts strongly to irritants and allergens, causing inflammation and flare-ups. -
Environmental Triggers:
Common triggers include pollution, harsh soaps, detergents, smoke, pollen, and pet dander. Sudden temperature changes can also worsen symptoms. -
Allergens and Irritants:
Certain fabrics (like wool), fragrances, or skincare products can trigger eczema in sensitive individuals. -
Stress and Hormonal Changes:
Emotional stress and hormonal fluctuations—especially in women—can cause flare-ups or make existing eczema worse.
3.jpg)
Treatment for Eczema
While eczema cannot be completely cured, it can be managed effectively with proper care and medical treatment.
1. Moisturizing and Skincare
-
Apply fragrance-free moisturizers regularly to lock in moisture.
-
Use gentle, hypoallergenic cleansers instead of soaps.
-
Avoid hot showers; opt for lukewarm water instead.
2. Medications
-
Topical Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and itching during flare-ups.
-
Antihistamines: Help relieve itching, especially at night.
-
Immunomodulators: Used for severe eczema that doesn’t respond to other treatments.
-
Antibiotics: Prescribed if skin infections occur.
3. Light Therapy (Phototherapy)
In some chronic cases, UV light therapy is recommended under medical supervision to reduce inflammation.
4. Lifestyle Changes
-
Identify and avoid personal triggers such as certain detergents or foods.
-
Wear loose, cotton clothing to prevent irritation.
-
Practice stress management techniques like yoga or meditation.
Need An Appointment?
Drop Your Number here
Conclusion
Eczema may not have a permanent cure, but with the right treatment plan, it can be effectively managed. Regular moisturizing, avoiding triggers, and following a dermatologist’s advice can help keep your skin calm, hydrated, and healthy. Remember — consistency in skincare and lifestyle habits is the key to long-term relief from eczema.
Patient's Testimonials
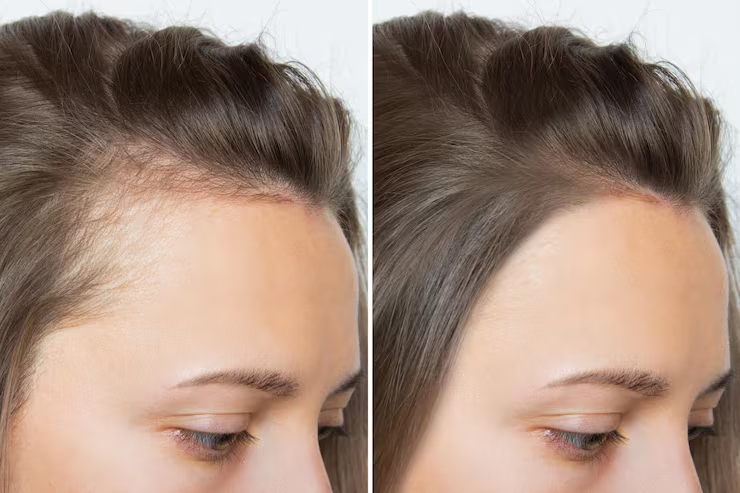

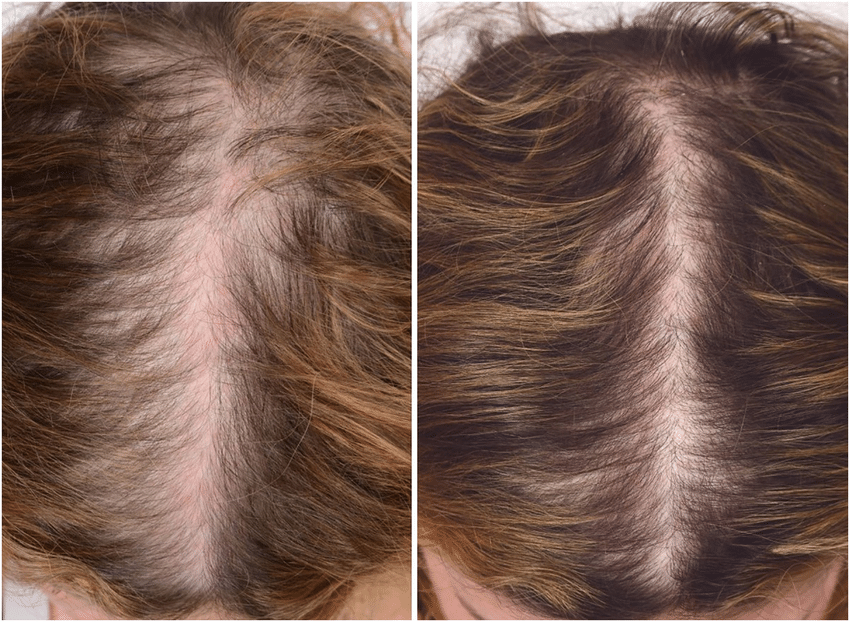
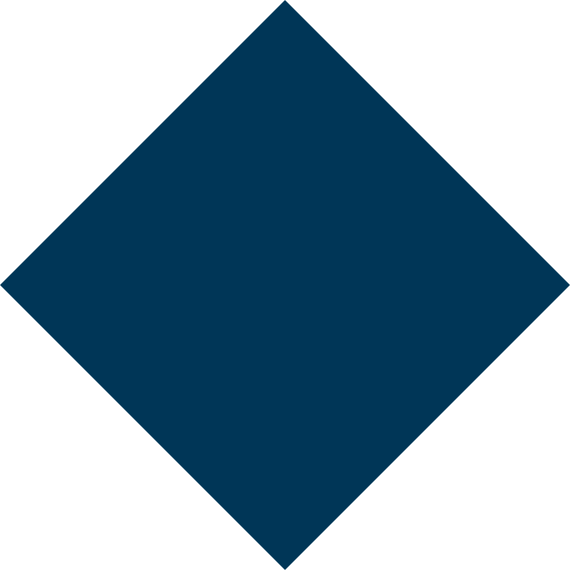
Reviews & Treatment Results at Bansal Skin Solution

5.0
(600 Reviews)

5.0
(500 Votes)

5.0
(567 Votes)
She's the best skin doctor I've come across so far. she listens patiently, gives the prominent treatment accordingly. Guys looking for skin treatment must visit Dr Nidhi Bansal, you will get satisfying results👍

Ravi Bhardwaj
PatientI consulted with Dr Nidhi Bansal after one of my friend suggested. The doctor is very calm and well versed with the solutions. I definitely liked the way He made me understand the issues of my hair sclap. I am very happy with my own experience with her and the treatment provided amazing hence I would highly recommend to this doctor for any skin or hair disease.

Manish Pal
PatientI was suffering from severe acne on my face. Dr Nidhi told me in detail about the treatment options and customized the procedures for my face. Within one day my redness and acne has reduced by 90%. I am so happy with the results and would recommend Dr Nidhi to everyone for their skin and hair problems.

Kartikey Singh
PatientBest doctor I always go to Dr Nidhi skin clinic whenever i have any skin problems . Dr. Nidhi is such a humble + trusted doctor I was dealing with pimples and scars from 6 years, someone told me about Dr Nidhi .I having been taking treatment from 2 months .my acne has gone for forever ,thanks for giving me normal skin best dermatologist in jaipur I got 100 % results , M bhut jayda preshan tha acne , blackheads whiteheads se ,mera face bhut khrab dikhta tha bhut guilty feel hota tha logo ko face krne m now I m confident .thank you doctor