Alopecia
Need An Appointment?
Drop Your Number here
Alopecia: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
Alopecia is a general term for hair loss that can occur on the scalp or any part of the body. It affects both men and women and can appear gradually or suddenly, depending on the cause. Hair loss can be temporary or permanent, and while it is not life-threatening, it often affects a person’s confidence and emotional well-being. Understanding the types, causes, and available treatments for alopecia can help individuals manage this condition effectively.
Types of Alopecia
1. Alopecia Areata
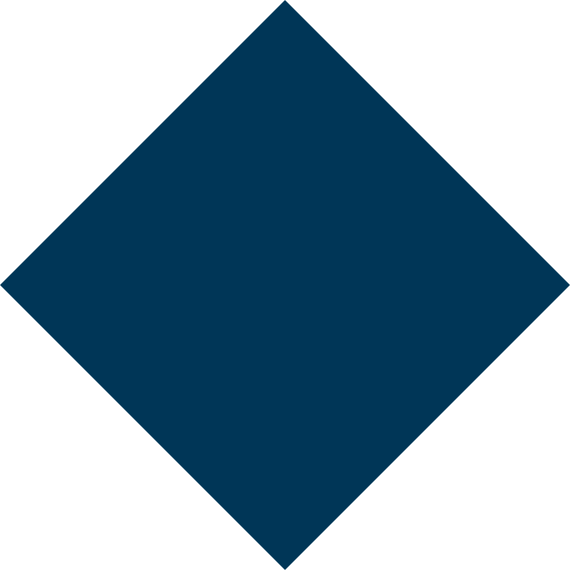
An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks hair follicles, causing round patches of hair loss. It can affect the scalp, eyebrows, or beard area and may sometimes progress to total hair loss.
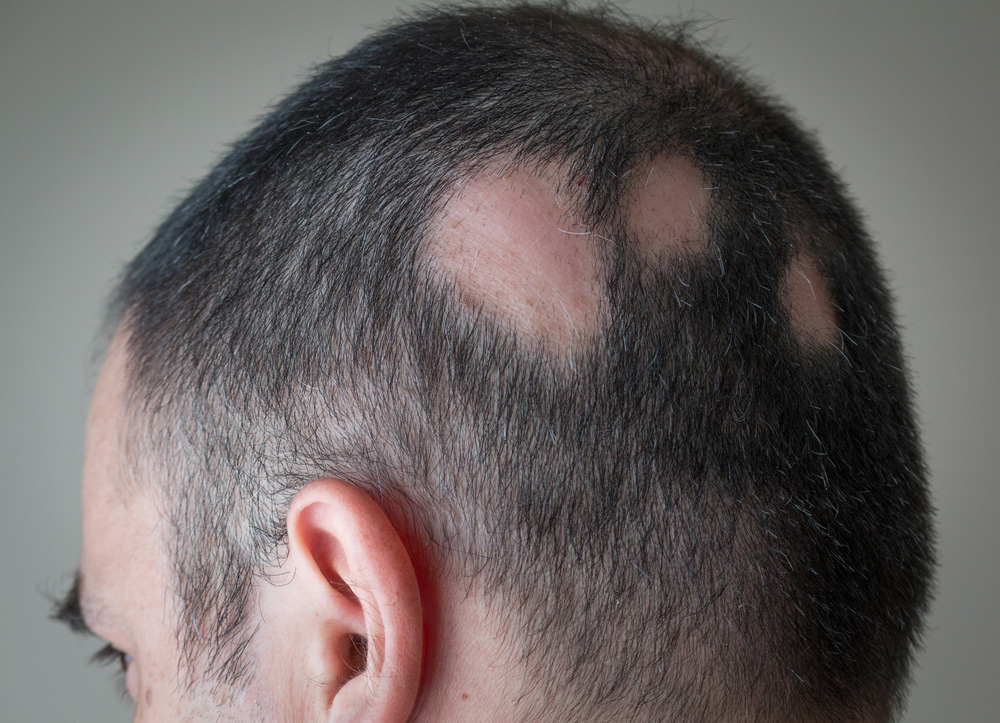
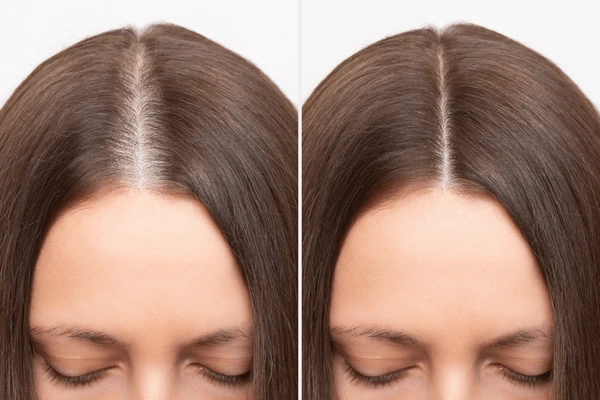
2. Androgenetic Alopecia
Also known as male or female pattern baldness, this is the most common form of hair loss. It results from hormonal changes and genetic predisposition. Men usually experience receding hairlines, while women often notice overall hair thinning.
3. Alopecia Totalis and Universalis
-
Alopecia Totalis: Complete loss of hair on the scalp.
-
Alopecia Universalis: Complete loss of hair on the entire body, including eyebrows and eyelashes.
These are rare but more severe forms of autoimmune hair loss.
4. Scarring (Cicatricial) Alopecia
This occurs when inflammation destroys hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss. It can result from skin infections, trauma, or certain skin disorders.
1.jpg)
Treatment for Alopecia
While some types of alopecia may resolve on their own, others need medical intervention. Treatment aims to slow hair loss, stimulate regrowth, and address the underlying cause.
1. Topical Treatments
-
Minoxidil (Rogaine): FDA-approved topical solution that stimulates hair follicles and promotes regrowth.
-
Corticosteroid creams: Help reduce inflammation in autoimmune alopecia.
-
Anthralin: A medicated cream used to treat patchy alopecia areata.
2. Oral Medications
-
Finasteride: Commonly prescribed for male pattern baldness to block hormone (DHT) responsible for hair loss.
-
Corticosteroid tablets: Used for severe autoimmune cases.
-
Immunosuppressants: Such as methotrexate or cyclosporine, to control immune system activity.
3. Injectable Treatments
-
Steroid injections: Directly injected into bald patches to encourage hair regrowth in alopecia areata.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP involves using a patient’s own blood plasma, rich in growth factors, to stimulate hair follicles. It has shown promising results in both alopecia areata and androgenetic alopecia.
5. Hair Transplant Surgery
In cases of permanent hair loss, surgical transplantation of hair follicles can restore a natural-looking hairline. This is best suited for pattern baldness.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Tips
Need An Appointment?
Drop Your Number here
Causes of Alopecia
Alopecia can be triggered by various internal and external factors, including:
-
Genetics: Family history of baldness or thinning hair.
-
Hormonal Imbalance: Especially during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders.
-
Autoimmune Reactions: The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles.
-
Stress: Physical or emotional stress can trigger temporary hair shedding (Telogen Effluvium).
-
Poor Nutrition: Lack of protein, iron, or essential vitamins weakens hair.
-
Medications: Certain drugs for cancer, blood pressure, or depression may cause hair loss.
-
Infections: Scalp infections like ringworm can damage hair follicles.
Alopecia is a complex but manageable condition. With the right diagnosis, medical treatment, and lifestyle care, many people can experience significant improvement in hair growth. Early intervention and professional guidance are key to minimizing hair loss and maintaining healthy, strong hair.
If you’re experiencing unusual or rapid hair loss, consult a dermatologist to find the best treatment tailored to your needs.
Patient's Testimonials
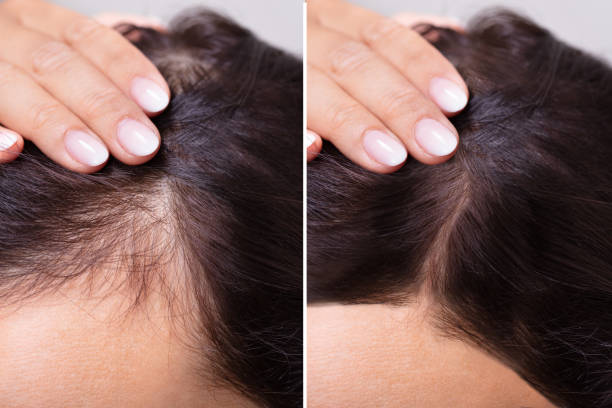

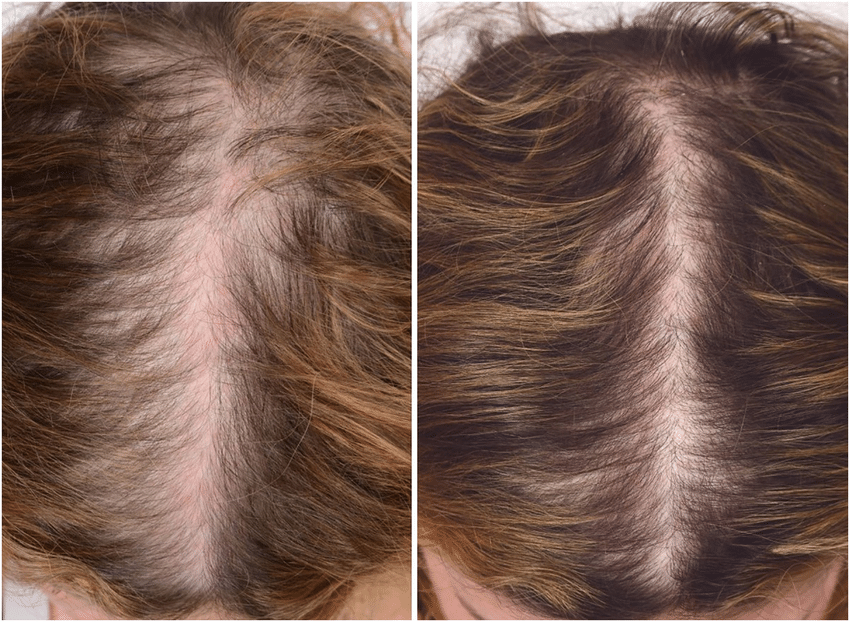
Reviews & Treatment Results at Bansal Skin Solution

5.0
(600 Reviews)

5.0
(500 Votes)

5.0
(567 Votes)
She's the best skin doctor I've come across so far. she listens patiently, gives the prominent treatment accordingly. Guys looking for skin treatment must visit Dr Nidhi Bansal, you will get satisfying results👍

Ravi Bhardwaj
PatientI consulted with Dr Nidhi Bansal after one of my friend suggested. The doctor is very calm and well versed with the solutions. I definitely liked the way He made me understand the issues of my hair sclap. I am very happy with my own experience with her and the treatment provided amazing hence I would highly recommend to this doctor for any skin or hair disease.

Manish Pal
PatientI was suffering from severe acne on my face. Dr Nidhi told me in detail about the treatment options and customized the procedures for my face. Within one day my redness and acne has reduced by 90%. I am so happy with the results and would recommend Dr Nidhi to everyone for their skin and hair problems.

Kartikey Singh
PatientBest doctor I always go to Dr Nidhi skin clinic whenever i have any skin problems . Dr. Nidhi is such a humble + trusted doctor I was dealing with pimples and scars from 6 years, someone told me about Dr Nidhi .I having been taking treatment from 2 months .my acne has gone for forever ,thanks for giving me normal skin best dermatologist in jaipur I got 100 % results , M bhut jayda preshan tha acne , blackheads whiteheads se ,mera face bhut khrab dikhta tha bhut guilty feel hota tha logo ko face krne m now I m confident .thank you doctor