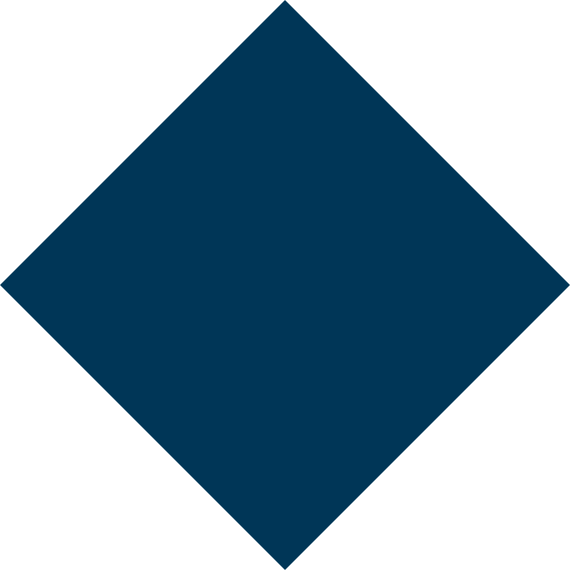
Skin Infection
Need An Appointment?
Drop Your Number here
Skin Infections: Causes, Types, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Skin infections are among the most common dermatological problems, affecting people of all ages. They occur when harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites invade the skin and cause inflammation, rashes, itching, or pain. While some infections are mild and heal on their own, others require medical attention to prevent complications or spreading. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you manage skin infections effectively.
Causes of Skin Infections
Skin infections are caused by different types of microorganisms, each leading to specific conditions:
-
Bacterial Infections:
Caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus, often entering through cuts or wounds.
Common examples include:-
Cellulitis
-
Impetigo
-
Boils (Furuncles)
-
-
Viral Infections:
Caused by viruses that infect the skin and sometimes spread through contact or air droplets.
Examples include:-
Warts (HPV)
-
Herpes simplex (cold sores)
-
Chickenpox
-
Shingles (Herpes zoster)
-
-
Fungal Infections:
Caused by fungi that thrive in warm, moist areas such as the feet, groin, or underarms.
Examples include:-
Ringworm (Tinea)
-
Athlete’s Foot
-
Fungal nail infections
-
Yeast infections
-
-
Parasitic Infections:
Caused by parasites living on or under the skin.
Examples include:-
Scabies (caused by mites)
-
Lice infestation
-
1.jpg)
Treatment Options for Skin Infections
Treatment depends on the type of infection and its severity:
1. Bacterial Infections
-
Topical antibiotics (e.g., mupirocin) for mild infections.
-
Oral or intravenous antibiotics for severe or widespread infections.
2. Fungal Infections
-
Antifungal creams or powders (like clotrimazole or ketoconazole) for mild cases.
-
Oral antifungal medications for stubborn or deep infections.
3. Viral Infections
-
Antiviral medications such as acyclovir for herpes or shingles.
-
Symptomatic relief with soothing creams or painkillers.
4. Parasitic Infections
-
Topical creams or shampoos to kill lice or mites.
-
Oral medications for severe infestations.
In all cases, maintaining hygiene and following the full course of treatment is essential to prevent recurrence.
Need An Appointment?
Drop Your Number here
Symptoms of Skin Infections
The symptoms of skin infections depend on the type and severity of the infection, but common signs include:
-
Redness or discoloration of the skin
-
Itching or irritation
-
Pain or tenderness in the affected area
-
Swelling or inflammation
-
Pus-filled blisters or bumps
-
Crusting or scaling of the skin
-
Fever or chills (in severe cases)
If left untreated, infections may spread to deeper layers of the skin or even to the bloodstream, causing more serious health issues.
Types of Skin Infections
-
Bacterial Skin Infections
-
Impetigo: Contagious infection causing honey-colored crusts, common in children.
-
Cellulitis: Painful redness and swelling, usually on the legs or arms.
-
Boils: Red, swollen bumps filled with pus, often caused by Staphylococcus.
-
-
Fungal Skin Infections
-
Ringworm: Circular rash with raised edges.
-
Athlete’s Foot: Itchy, cracked skin between toes.
-
Candidiasis: White patches or redness in moist areas.
-
-
Viral Skin Infections
-
Warts: Small rough bumps caused by HPV.
-
Herpes simplex: Painful blisters around the mouth or genitals.
-
Shingles: Painful rash with blisters, caused by the chickenpox virus reactivation.
-
-
Parasitic Skin Infections
-
Scabies: Intense itching caused by mites burrowing under the skin.
-
Lice: Itchy scalp caused by head lice infestation.
Home Care and Prevention Tips
To prevent and manage skin infections:
-
Keep skin clean and dry.
-
Avoid sharing personal items like towels, razors, or clothing.
-
Wear breathable clothing to prevent moisture buildup.
-
Treat cuts and wounds promptly with antiseptics.
-
Avoid scratching infected areas.
-
Maintain a healthy diet to boost immunity.
-
Use sunscreen to protect skin from sun damage.
-
You should consult a dermatologist if:
-
The infection spreads rapidly or is painful.
-
You develop fever, chills, or pus-filled sores.
-
Over-the-counter treatments are not helping.
-
You have diabetes or a weak immune system.
-
Early diagnosis ensures faster recovery and prevents complications.
Conclusion
Skin infections are common but manageable with timely treatment and proper care. Whether caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, or parasites, understanding the type and cause helps in choosing the right therapy. Maintaining good hygiene, protecting your skin, and consulting a dermatologist early are the best ways to ensure healthy, infection-free skin.
When to See a Dermatologist
-
Patient's Testimonials
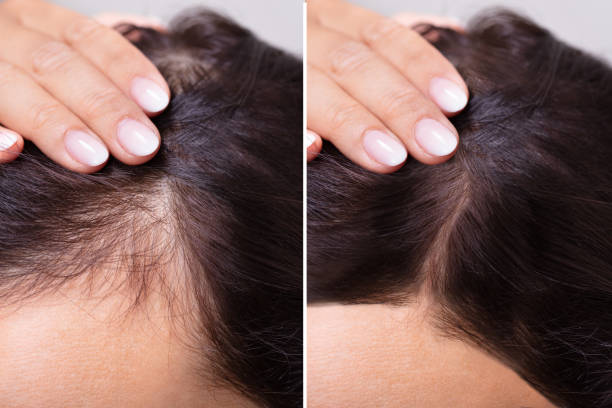

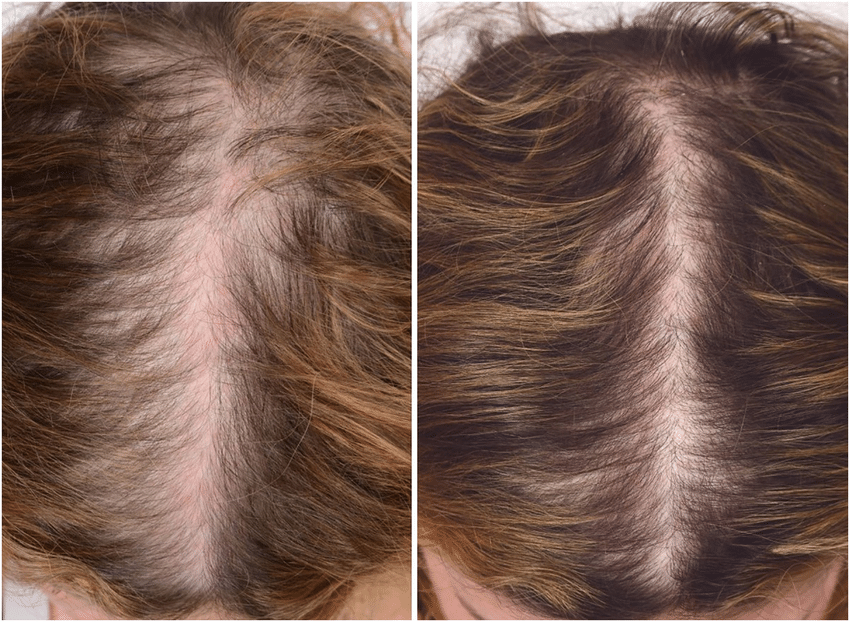
Reviews & Treatment Results at Bansal Skin Solution

5.0
(600 Reviews)

5.0
(500 Votes)

5.0
(567 Votes)
She's the best skin doctor I've come across so far. she listens patiently, gives the prominent treatment accordingly. Guys looking for skin treatment must visit Dr Nidhi Bansal, you will get satisfying results👍

Ravi Bhardwaj
PatientI consulted with Dr Nidhi Bansal after one of my friend suggested. The doctor is very calm and well versed with the solutions. I definitely liked the way He made me understand the issues of my hair sclap. I am very happy with my own experience with her and the treatment provided amazing hence I would highly recommend to this doctor for any skin or hair disease.

Manish Pal
PatientI was suffering from severe acne on my face. Dr Nidhi told me in detail about the treatment options and customized the procedures for my face. Within one day my redness and acne has reduced by 90%. I am so happy with the results and would recommend Dr Nidhi to everyone for their skin and hair problems.

Kartikey Singh
PatientBest doctor I always go to Dr Nidhi skin clinic whenever i have any skin problems . Dr. Nidhi is such a humble + trusted doctor I was dealing with pimples and scars from 6 years, someone told me about Dr Nidhi .I having been taking treatment from 2 months .my acne has gone for forever ,thanks for giving me normal skin best dermatologist in jaipur I got 100 % results , M bhut jayda preshan tha acne , blackheads whiteheads se ,mera face bhut khrab dikhta tha bhut guilty feel hota tha logo ko face krne m now I m confident .thank you doctor